Deployment and Instance Management
Deployment and Instance Management
This section is all around how to deploy and manage code, applications, and machines
Elastic Beanstalk
Beanstalk = PaaS, it helps us deploy and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Like actual full stack web applications with backend, frontend, DB, etc...
You'll still need to write and manage your application code, but Beanstalk handles the deployment, capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling, and application health monitoring
- Elastic Beanstalk is a developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
- Helpful for porting on-prem to cloud with minimal changes
- If you can dockerize your container, you can deploy on Beanstalk
- Beanstalk meant to "replatform" apps
- Supports many platforms: Go, Java w/ Tomcat, Python, Node.js, anything Dockerized really, etc...
- It's basically just a wrapper around a number of other services, and it's all displayed in one view
- Beanstalk is free, but you pay for underlying infra
- Management:
- Instance config, OS, and general deployment compute hadled by beanstalk
- App code is responsibility of developer
- Three architecture mdoels:
- Single instance deployment is good for dev
- LB + ASG good for prod / pre-prod web apps
- ASG good for non web-apps (workers, backend services, etc)
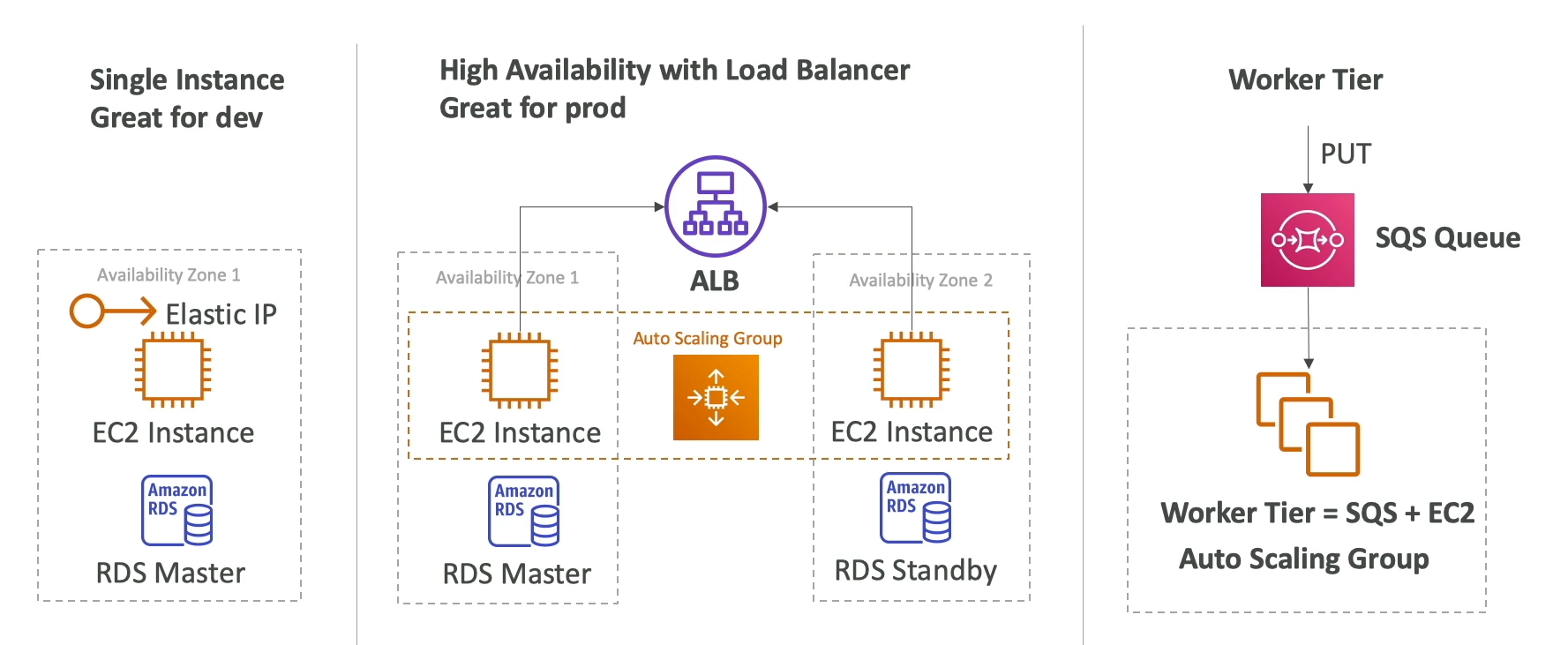
- Web Server vs Worker:
- Any decoupling ==== SQS!!!
- App performs long running tasks to complete, then offloadnig them to dedicated workers is typically used
- Decoupled beanstalk can help us manage web app and worker environment
- Blue / Green Deployment
- Can use a new environment (green) and validate independently
- Use Route53 weighted routing to redirect small amounts of tradffic to Green, and shift over time
- Beanstalk "Swap URLS" DNS Swap feature
- Parameters
- Environment properties
- Key/Value pairs that are passed to app as env variables
- Environment
- Manages size of instances, scaling policies, rolling updates, etc...
- Application versions
- Each deploy is a new application version
- Stored in S3 bucket
- Can roll back to previous versions easily
- Monitoring
- Integrated with CloudWatch
- Health status of instances and app
- Enhanced health monitoring for more metrics and data
- Environment properties
Code Deploy
- Helps us to Deploy code!
- Deploy new versions of code to EC2, Docker containers on ECS, etc...
- Ansible, Terraform, Chef, Puppet, etc... are useful, but can use AWS CodeDeploy out of the box with EC2, ECS, ASG, and Lambda
- Does in-place update of fleet of EC2 instances
- Can use hook to verify the deployment after each deployment phase
- CodeDeploy fulls manages take down, in place updaets, and having V2 rolled out on EC2's
- EC2 Update types:
- In-place updates:
- Updates current EC2 instances
- Instances newly created by ASG will automatically get automated deployment
- Blue/Green deployment
- New ASG is created for V2, and new launch templates are used
- CHoose how long you keep old instances
- Start routing traffic to V2
- Requires ELB
- CodeDeploy will slowly remove old instances and keep new ones
- In-place updates:
- CodeDeploy to Lambda
- Traffic shifting feature
- Pre and Post traffic hooks to validate deployments
- These are just more lambda functions to run before and after deploying new code
- Easy and automated rollback using CWatch Alarms
- CodeDeploy can rollback if CWatch alarms go over threshold
- SAM framework natively uses CodeDeploy
- CodeDepoy to ECS
- Support B/G deployment on ECS and Fargate
- Setup is done on ECS Service definition, not on CodeDeploy UI
- New task set is created and traffic gets rerouted to new task set
- If everything is good for X minutes the old task set is terminated
- Supports Canary deployment
10Percent5Minutes - CodeDeploy just ensures that ECS Task definitions get shifted over time, and then ensures stability
CloudFormation
- Brings IaC into AWS
- Helps to port across accounts and regions
- Backbone of:
- Beanstalk
- Service Catalog
- SAM (Serverless App Model)
- Retain data on deletes
- DeletionPolicy
- Can use on any resource to control what happens when a template is deleted
- Retain
- Specifies a resource to preserve upon deletion
- Snapshot
- EBS, RDS, ElastiCache, Redshift, DBCluster, etc
- Delete
- Same as above, but for S3 you need to delete everything inside of it first
- DeletionPolicy
- CustomResources
- Can define a custom resource to address any challenges from native CF
- Backed by lambda function to CRUD resources
- Empty S3, Get AMI, etc!
- StackSets
- CRUD stacks across multiple accounts and regions
- Basically a module
- Admin to create stack sets
- Updating a stack set means updating all instances from there, throughout all accounts and regions
- Enable AutomaticDeployment feature to auto deploy to accounts in AWS Orgs or OU's
- Drift
- What happens if someone manually alters the resources?
- CF Drift compares all resources to state file
- Can be done on entire stacks, or an individual stack
- Secrets Manager
- Can set and use secretsin CF natively
- Can help us ensure that whenever a secret rotates, the value sitting in other resources such as RDS will automatically update
- Can handle imports into individual, or entire stacks
- Need to create a template that describes the entire stack including currently tracked resources, and newly desired imported resources
AWS Service Catalog
- For users new to AWS who have too many options
- Allows users to access a self-service portal with authorized access
- Bascially allows users to see pre-authorized resources defined by admins, and then helps them to deploy apps using those resources
- Admins use CloudFormation templates to create stacks which are approved stacks!
- Allows IAM perms to access the stacks
- Users can then launch the products with variable naming abilities
- Stacks assigned to portfolios (teams)
- Teams are presented a serlf-service portal to launch products
- All deployed products are centrally managed
- Helps w/ governance, compliance, and security
- Integrates with 3rd party portals like ServiceNow
Serverless Application Model (SAM)
- Framework for developing and delpoying serverless apps
- All configs are done via YAML code
- Lambda, DynamoDB, API GW, Step Functions, etc
- SAM can use CodeDeploy to deploy lambda functions
- Uses CFormation on backend to deploy
- CICD Arch
- CodePipeline for DevOps CICD
- CodeCommit for git style version control
- CodeBuild for build, test, package
- CloudFormation + SAM for sending to CodeDeploy
- CodeDeploy helps to shift traffic on lambdas
- CodePipeline for DevOps CICD
- Just need to remember SAM uses CodeDEploy on backend for lambdas
AWS CDK
- Cloud Development Kit
- Define clodu infra using familiar language (Python, JS, Java, etc..)
- When you don't want to use CF directly with YAML
- After writing CDK it will compile into CFormation YAML
- Allows for for loops, file access, and other things that YAML can't handle
AWS SSM
- Helps to manage cloud and on-prem VM's
- Need to install SSM agent, or use AMI with it pre-installed
- Installed by default on AWS Linux AMI + some Ubuntu AMI
- Works for Windows and Linux
- If an instance can't be controlled with Systems Manager, it's probably an issue with the agent
- What can SSM do?
- Allows us to run commands over One:Many instances
- Allows for scripting and updating of hundreds of instances across cloud and on-prem
- Integrated with IAM and CloudTrail
- No need for SSH!
- Allows up to 5 admins to connect to 1,500 instances concurrently
- Rate Control (how fast to run over instances) + Error control (what to do on failure)
- SSM agent ensures all of this can be done on the machine from calling party
- Common use cases:
- Send command before an ASG instance is terminated
- Can allow some lifecycle hook to run before an EC2 instance is terminated / deleted
- When EC2 goes into
Terminating:Waitstate, it will notify EventBridge which can call SSM Automation on the EC2 instance itself to run some final commands before shutting downSendCommandis sending a command to the EC2 instance
- At this point our Lifecycle Hook can shut the instance down
- Send command before an ASG instance is terminated
- Patch Managers
- Helps
- Define a Patch Baseline to use (or multiple if needed)
- Define Patch Groups:
- Can define based on:
- Tags
- Name
- Region
- etc
- Can define based on:
- Define Maintenance Window for schedule duration, registered groups, and registered tasks
- Run
AWS-RunPatchBaselineRun Command which runs on Windows and Linux- Rate Control: How many instances to run at a time - concurrency and parallelism
- Error Control: What to do on errors
- Monitor Patch Compliance using SSM Inventory
- Session Manager
- Allows for secure shell to EC2 and on-prem without opening port 22 and using SSH keys
- Can just use UI based shell where Systems Manager is taking care of connecting and authentication
- All commands logged and can be sent to S3 or CloudWatch
- Can use CloudTrail to see
StartSessionevents
- OpsCenter
- Resolve Operational Issues (OpsItems) related to AWS resources
- Issues, Items, and Alerts
- Aggregates information to resolve issues on each OpsItem such as:
- AWS Config changes and relationships
- CloudTrail Log
- CloudWatch Metrics
- CloudFormation Stack info
- Across all these groups you can use Automation Runbooks via SSM Runbook Automations to resolve the incidents
- EventBridge and CloudWatch Alarms can create OpsItem events
- Resolve Operational Issues (OpsItems) related to AWS resources
AWS Cloud Map
- Fully managed resource discovery service
- Helps with service discovery / DNS routing + redeployment
- Moving from V1 to V2 of a backend service from a frontend service
- Creates a map of your backend services / resources that app depends on
- You register your application components, their locations, attributes, and health to AWS CloudMap
- Acts as a ZooKeeper-esque service discovery mechanism and helper
- Integrations with Health Checking to stop sending traffic to unhealthy endpoints
Workspaces
- Managed, secure, cloud desktop
- Connect to virtual desktop from laptop, and that virtual desktop connected to corporate data center or cloud
- Great to eliminate management of on-premise VDI's
- integrated with MS Active Directory
- Pricing on-demand or monthly
- Secure, encrypted network isolation
- Cross region redirection
- Allows us to redirect users via Managed Microsoft AD for failover
- Healthcheck and failover for high availability
- User data is region specific though
Workspace Application Manager
- Dep and manage applications as virtualized app containers
- Provision at scale, and keepa pp updates using WAM
- Windows Updates
- By default workspaces are configured to install software updates
- Workspaces with Windows has Windows Updates turned on
- Full control if you want to turn it off
- Define maintenance windows
- Always on (
00h00 to 04h00) - Autostop would run this once a month
- Always on (