Databases
This whole fuckin section is going to be on serverless Dynamo I bet
DynamoDB
- NoSQL DB, fully managed, massive scale (1M req / sec)
- Similar architecture to Apache Cassandra
- No disk space, max object size is 400KB
- Anything larger store in S3 and store reference in DynamoDB
- Capacity and provisioning
- Write Capacity Unit (WCU): Governs write throughput
- 1 WCU = 1 write per second for an item up to 1KB in size
- Item larger than 1KB consumer more than 1 WCU, and it's always rounded up
- Dynamo Streams does not consume WCU's
- Read Capacity Unit (RCU): Governs read throughput
- 1 RCU = 1 strongly consistent read, or 2 eventually consistent reads per second
- For items up to 4KB in size
- DynamoDB Streams also does not consume RCU
- Only direct reads and writes from DynamoDB consume W/R CU's
- Autoscaling
- On Demand
- Write Capacity Unit (WCU): Governs write throughput
- Supports CRUD ops
- Read:
- Eventually consistent
- Strongly consistent
- Supports ACID transactions across multiple tables
- Backups available with Point In Time (PIT) recovery
- Table classes:
- Infrequent
- Standards
DyanmoDB Basics
Most of these basicas are covered in the NoSQL Walkthrough
- Made of tables
- Each table has a Primary key
- Primary Key is either Partition Key, Partition and Sort Keys, or Combo Key
- Must be decided during creation time
- Responsible for hash calculation and partitioning
- Options:
- Partition Key only (hash)
- Partition key must be unique per item
- Must be "diverse" so that data partitions are uniform, no hot partitions
- Partition Key + Sort Key
- Combo of 2 must be unique
- Data grouped logically by partition key
- Sort Key AKA Range Key
- Timestamp usually good for sort key
- Partition Key only (hash)
- Each table can have an infinite number of items (infinite number of rows)
- Each item has attributes
- Can change and evolve over time
- Can be NULL
- This is how we get to "schemaless" and not a rigid SQL schema
- Max item size is 400KB
- Data Types:
- Scalar: String, Num, Boolean, etc
- Document: List, Map
- Set: String Set, Number Set, etc,...
- Indexes:
- Object = Partition Key + Optional Sort Key + Attributes
Local Secondary Index:- Keep the same Primary Key
- Select an alternative Sort Key
- Must be defined at table creation time
- Can use index inside of partition, it's local so doesn't go across partitions
Global Secondary Index:- Can change Primary Key and Optional Sort Key
- Completely new index
- Can be defined after
- Spans all partitions, would be basically new memory across entire cluster
Features
TTLcan automatically expire row after a specified epoch dateDynamoDB Streams- React to changes to DynamoDB tables in real time
- Basically CDC Stream
- Can be read by Lambda, and probably other services
- Forward to OpenSearch, Kineses
GlobalTables(cross region replication)- Active active replication, many regions
- Can CRUD on any of the replicas, and it will get replicated to all other DynamoDB clusters on other regions
- Must enable DynamoDB Streams
- i.e. it's CDC based replication
- Useful for low latency DRecovery purposes
- Active active replication, many regions
- Kinesis Data Streams for DyanmoDB
- Called it up there
- Can use Kinesis streaming from CDC based Streams on Dyanmo
- Sounds like it's a managed equivalent to Debezium CDC + Kafka
- Use Kinesis Data Streams to capture item-level changes in DynamoDB
- Can use Kinesis Firehose to read the data and store it wherever
- Can use Kinesis Data Analytics for real time filter, agg, transform transformations and write that back to DStreams, to Firehose, or other services
- Sounds like Firehose and Data Analytics are managed services off of Flink or Samza, but they abstract it into diff services
- Custom and longer data retention period (24 hr in DB Streams), but long term storage in other services
- DynamoDB Accelerator: DAX
- Cache for DynamoDB
- No app rewrite at all, app still GET or PUT, and caching handled by DAX
- Solves hot key problem
- 5 min TTL
- Multi AZ (3 nodes min for prod)
- Encryption at rest
- DAX vs ElastiCache
- Use DAX when a client directly wants to access DynamoDB and doesn't want to interact wiht other caches / services
- DAX good for both individual object caches and query / scan caching
Solution Architecture - Indexing
- S3 does not have the best search functionality, and there's lots of info that S3 has problems going through
- A common scenario is that on S3 events, we trigger a lambda and that lambda will update a DynamoDB table that acts as an index on multiple different attributes
- This allows us to:
- Search by date
- Get metrics and aggregations like total storage used by a customer
- List all objects with certain attributes
- Find all objects within some date range
OpenSearch (ElasticSearch)
- Renamed from ElasticSearch to OpenSearch
- Fork of ES b/c of licensing issues
- OpenSearch Dashboards === Kibana Dashboards for ElasticSearch
- Managed vs Serverless
- Managed allows us to choose more granular controls over infra
- Use cases:
- Log analytics
- Real time app monitoring
- Full text search
- Clickstream analytics
- Indexing
- Suite:
- OpenSearch:
- Search and indexing capabilities
- OS Dashboards:
- Monitoring and metrics of OS data
- Logstash:
- Log ingestion mechanism
- Alternative to CW Logs where we can decide retention and granularity
- OpenSearch:
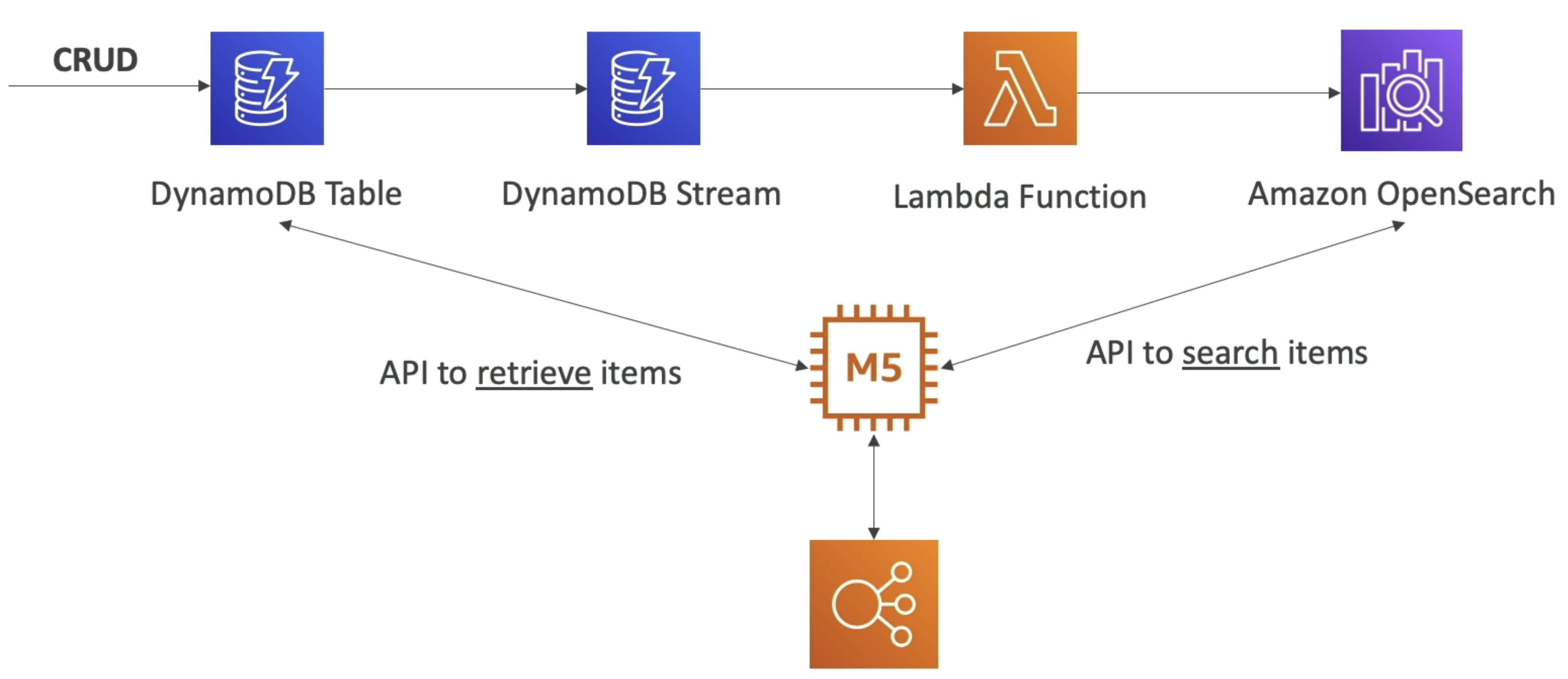
- OpenSearch + Dynamo or CW
- Common pattern is CRUD ops into DynamoDB
- DynamoDB Streams for CDC
- Lambda or Kinesis for computing over streams
- Send CDC data to OpenSearch
- Allows for search API's over data sitting in DynamoDB
- Full text search, similarity, traversal, etc...
- Then use response from OS to GET data from DynamoDB
- Can do the same thing but have CloudWatch and send logs to OSearch
- Lambda for real time
- Kinesis for near real time (it does batching)
- Allows for more robust search over logs
RDS
- Relational Database Service
- Engines:
- MarioDB, Postgres, MySQL, IDM DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server
- Managed Service so provisioning, backups, patching, monitoring, etc all covered
- Deployed in a VPC, usually private
- Lambda that wants access needs to be deployed in private VPC since lambda and other serverless services are deployed on AWS
- Storage by EBS, and can increase volume size automaitcally via auto-scaling
- Backups allow PIT recovery, and they expire
- Snapshots are manual, and can help DR plans and send full databases across regions
- RDS events send events similar to S3 to SNS
- Not CDC, events like operations, outages, etc...
- Multi AZ + Read Replicas
- Multi AZ
- Standby instance in case of outage
- R/W only on leader DB
- Synchronous replication
- Read Replicas
- Helps increase throughput
- Eventual consistency via asynchronous replication
- Reads can go anywhere, writes only to leader
- Route53 helps us to route traffic to distribute over RR's without needing PGBouncer or other tools
- Can use Route53 health checks to ensure our RR's are still available, and R53 can alter route sets if a health check fails
- Multi AZ
- Security
- KMS encryptuion at REST for underlying EBS volumes / snapshots
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for Oracle and MS SQL Server
- SSL encryption to RDS is possible for all DB in-flight
- Security groups help for firewall and whitelisting
- IAM authentication to MySQL, Postgres, and MariaDB
- Authorization still happens within RDS
- Need to tie users to abilties inside of DBase
- Authentication happens via IAM and RDS API calls
- Auth token lifetime of 15 minutes
- Only used for connecting
- RDS Service provieds auth token
- Can copy un-encrypted RDS to encrypted one
- Can go back and forth via Snapshots
- CloudTrail can't track queries
- RDS for Oracle gotchas:
- RDS backups for backups & restores to RDS for Oracle
- Oracle RMAN recovery manager is for backups, the restores RMAN provides cannot be used to restore to RDS, it only provides restores to non-RDS databases
- Real Application Clusters (RAC)
- RDS Oracle does not support RAC
- To get RAC you need to install Oracle on EC2 instance where we have full control
- RDS for Oracle supports Transparent Data Encryption to encrypt data before it's written to storage
- DMS works on Oracle RDS
- On-prem Oracle DB DMS RDS Oracle
- Allows us to replicate DB's, common pattern is replicating an on-prem DB to cloud one
- RDS backups for backups & restores to RDS for Oracle
- RDS for MySQL gotchas:
- Can use
mysqldumpto migrate RDS DB to non RDS- External MySQL DB can run on prem or EC2 or wherever
- RDS Proxy for AWS Lambda
TooManyConnectionsexception sometimes when we use Lambda functions with RDS since they open and maintain connections- RDS Proxy can take care of cleaning up idle connections, managing connection pools, etc.
- Supports IAM Auth
- RDS Proxy is a service outside of RDS itself - it can be deployed in other subnets if needed
- Can use
Solution Architecture - Cross Region Failover
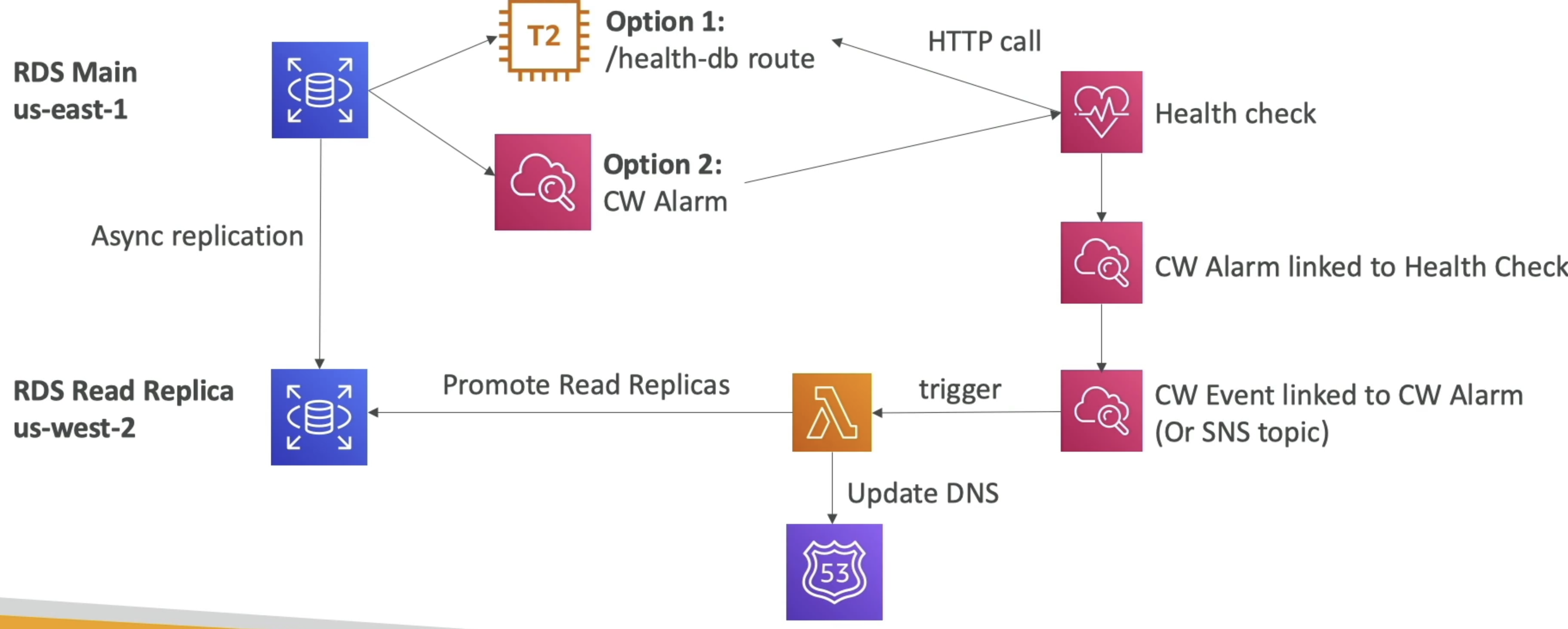
- Can use RDS events and CW health checks together to get notified of downed RDS clusters
- These CW Events or RDS events or anything else can trigger lambdas that update DNS and promote read replicas to leader
- Can't use DNS health checks only because we need to promote RR to leader, and that can't be done without custom logic stored in lambda
Aurora
- Engines: Postgres compatible and MySQL compatible
- Storage automatically frows by 10GB increments to 128TB max
- 6 copies of data across multi AZ by default
- Up to 15 RR's
- Cross region RR entire database is copied
- Load / offload data directly to / from S3
- Backup, Snapshot, and Restore exactly same as RDS
HA and Scaling
- Peer to peer replication + durability is fully discussed in KV Store Deep Dive Peer to Peer
- 6 copies of data across 3 AZ's
- 4 out of 6 needed for writes
- 3 out of 6 for reads
w = 3, r = 4, n = 6, w + r > n- Self healing with peer-to-peer replication
- Storage striped across 100's of volumes
- Single leader for writes, 15 RR followers
- Auto failover of leader in < 30 seconds SLA
- All RR's able to serve reads
- Aurora Cluster: Read and Write
- Read and Write endpoints for client app
- Shared volume auto expanding storage underneath
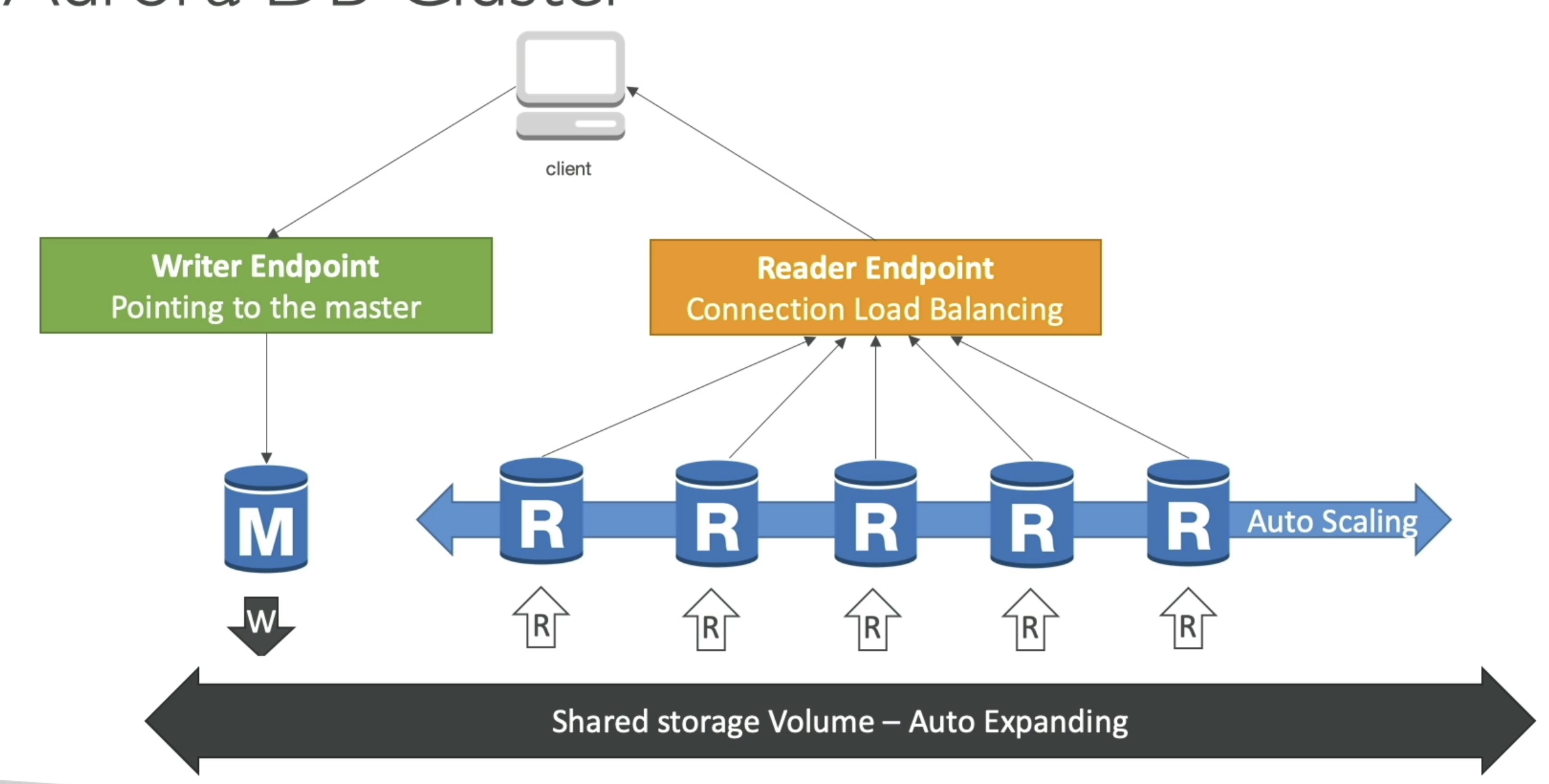
- Aurora Endpoints
- Endpoint = cluster address + port
- Write Endpoints
- Connects to primary and is used for all write ops
- Reader Endpoints
- Does load balancing for read only cnxnx
- Only for read queries
- Custom Endpoints
- Represents a set on DB instances that you choose in Aurora cluster
- Use when you want to connect to specific subset of DB's with different capacities / configs
- Basically when different DB's in cluster have different DB parameter groups, we can use custom endpoint to only reach those RR's
- Instance Endpoints
- Connects to specific DB instance in Aurora Cluster
- Use for diagnosis or fine tuning of one specific instance
Logs
- Can monitor the following log files:
- Error
- Slow query
- General
- Audit
- Downloaded or published to CW Logs
- Troubleshooting:
- Can use performance insights tool
- Waits, SQL Statements, Hosts, and Users
- Helps to see if specific actors / queries are hogging resources
- CW Metrics:
- CPU
- Memory
- Swap usage
- Enhanced monitoring metrics at host / process level
- Go through logs
- Can use performance insights tool
Aurora Serverless
- From client perspective you just access 1 single proxy fleet endpoint
- It scales nodes and volumes for you
- Access Aurora Serverless with simple API endpoint
- No JDBC connections needed
- Proxy fleet endpoint manages connections
- Secure HTTPS endpoints to run SQL Statements
- Users need access to Data API and Secrets Manager
- RDS Proxy
- Allows us to create our own proxy for read only replicas if we desire
- Global Aurora
- 1 primary region
- 5 secondary regions for read only
- Replication lag is < 1 second SLA
- Good for Disaster Recovery and decreasing latency next to users
- Write forwarding
- Secondary DB clusters can forward writes made to them to primary DB cluster
- Allows all nodes to accept write queries, but only primary does the actual computations
- Reduces # of endpoints to manage, and all apps can just send reads and writes to the endpoint they know
RDS To Aurora
- Can take snaoshot into S3 and restore to Aurora DB Instance
- Create Aurora RReplica on RDS DB Instance
- Gets replicated via synchronous replication
- Once it's replicated, just promote it