Typical Frontend
This is one of the common components we'd use across products, and is comprised of a static name / IP for a load balancer and some services
Architecture
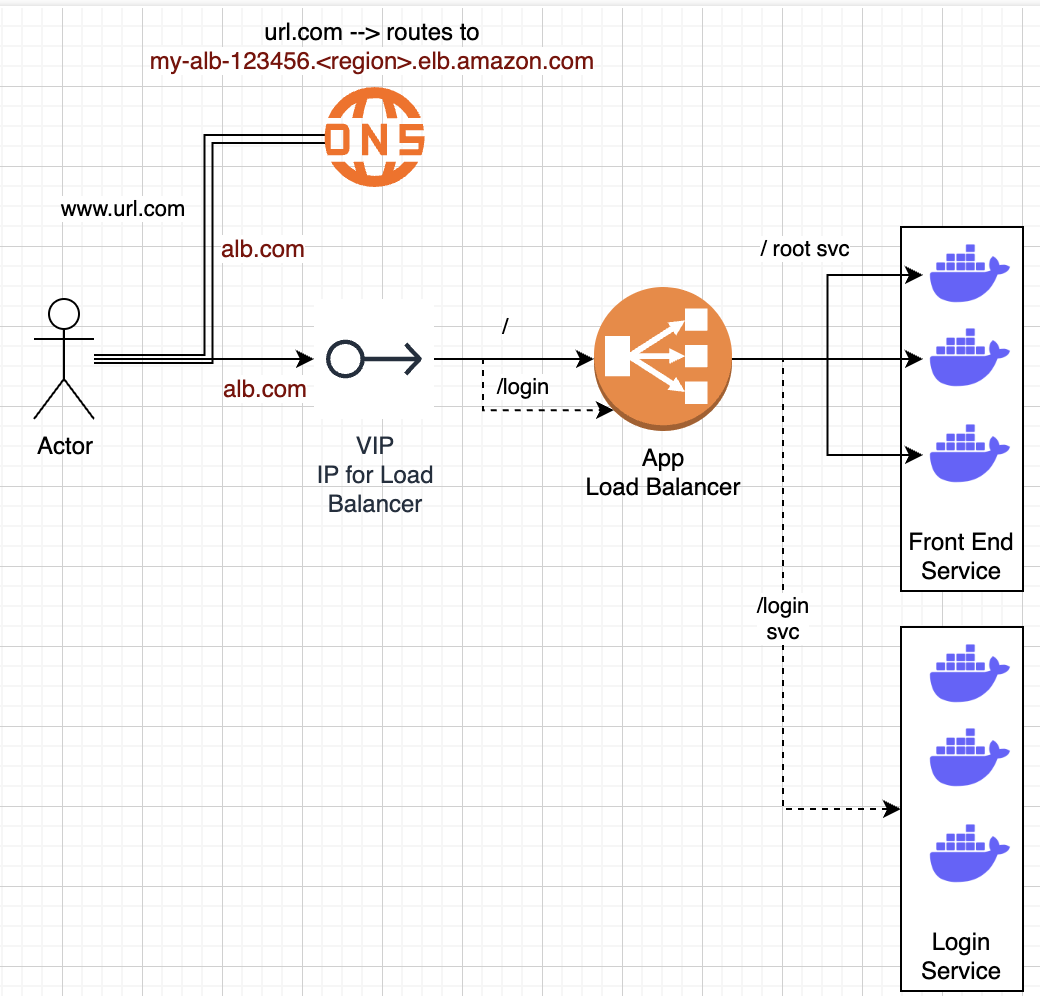
VIP
Virtual IP (VIP) is an IP address not tied to a physical network interface
- On AWS we can think of Elastic IP for network load balancer
- Basically allows clients to connect to a single IP address
Requirements:
- Stable endpoint, whether it is IP address or URL
- Connects to a load balancer
- Load Balancer is then able to route requests
AWS:
-
Network Load Balancer: Works on Layer 4 (IP address, port) routing
- Can assign NLB an Elastic IP (unchanging IP address) via the Network Interface of the NLB
- If you see fit you can have some Route53 DNS resolution for
url.comto that ElasticIP
- If you see fit you can have some Route53 DNS resolution for
- Then for any service that spins up in AWS you'd need to make those services a target from NLB
- ServiceA has IP 1.1.1
- If a client goes to NLB:80 --forward_to--> 1.1.1:80
- ServiceB has IP 1.1.2
- If a client goes to NLB:90 --forward_to--> 1.1.2:80
- ServiceA has IP 1.1.1
- Can assign NLB an Elastic IP (unchanging IP address) via the Network Interface of the NLB
-
Application Load Balancer:
- Works on Layer 7:
- (url.com/param1) with URL parameters
- Headers
- HTTP Parameters
- Also helps us route to dynamically scaling ECS / EKS instances
- Route53 DNS record can map to ALB DNS name
url.comcan route tomy-alb-123456.<region>.elb.amazon.com
- Similar to above, except we register services and instances instead of IP addresses
- If a client goes to
url.com/register--forward_to--> ECS registration service with 1:Many instances running - Still need to register port information that ECS containers would be listening to, along with ensuring security group routing rules
- If a client goes to
- Works on Layer 7: