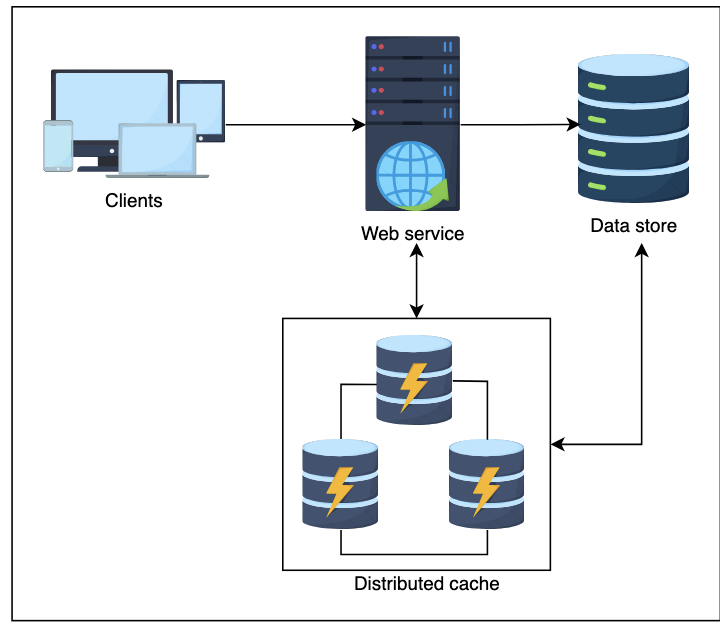
Distributed Cache
Distributed Cache
A cache is an intermediary component that helps to store "hot keys" so that the main database(s) aren't constantly bombarded to retrieve popular items
They help to alleviate pressure by serving frequently accessed items in memory, and allowing web servers to respond using these values versus the core database values
They are especially useful for data with infrequent write updates, and they can cause inconsistencies when the main database is updated and the cache is not
One of the toughest parts of software engineering is cache invalidation, and it's the trade-off of when to remove a value from the cache versus continuing to resuse it. There's a tradeoff in consistency, latency, and complexity in a system.
When a service is able to find the key in the cache it's known as a cache hit, and it will use that value, but if it cannot find it it's known as a cache miss
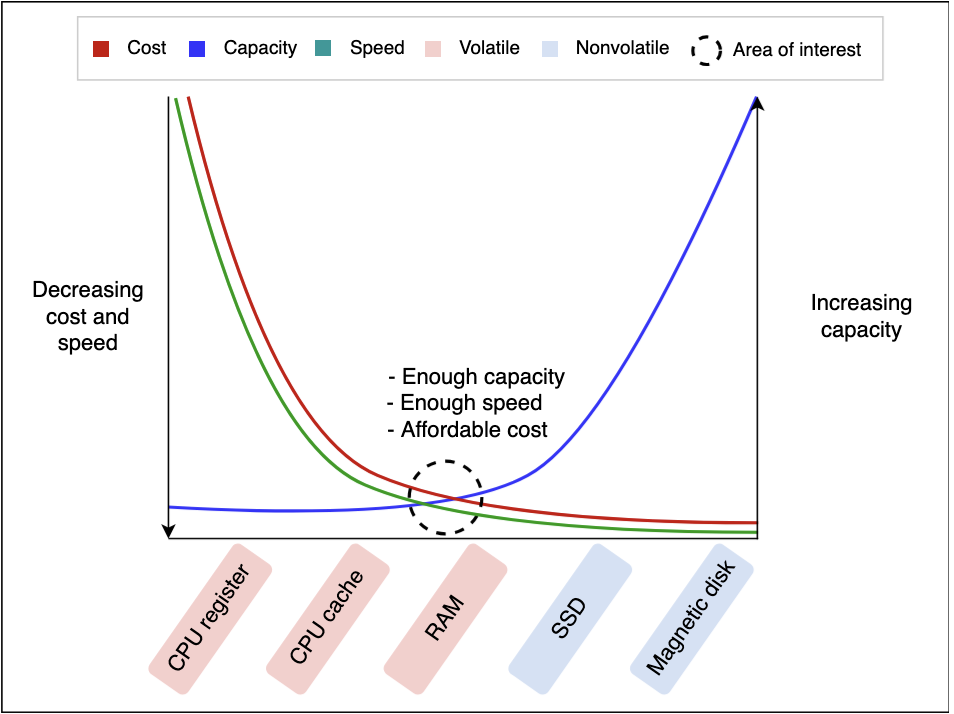
Most cache's will use RAM as it has the most convenient trade-offs in terms of capacity and speed
- SSD's and Magnetic Disks have larger capacity, but they're much slower
- CPU cache and register are faster, but have much lower capacity
The only difference with distributed caches is that there are multiple nodes in the cache cluster to store frequently accessed data, and it helps to scale and guarantee a higher degree of availability
Caching can be:
- Servers closer to the user (CDN / caching content locally on browser)
- A RAM based database (Redis / Memcache) for serving data faster
- Anything else that helps to facilitate getting popular data to end users without querying main data stores
There are also different layers - servers closer to user are the Web Layer, where getting data from Redis is closer to Application Layer
| System Layer | Technology in Use | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Web | HTTP cache headers, web accelerators, key-value store, CDNs | Accelerate retrieval of static web content, manage sessions |
| Application | Local cache and key-value data store | Accelerate application-level computations and data retrieval |
| Database | Database cache, buffers, key-value data store | Reduce data retrieval latency and I/O load from database |